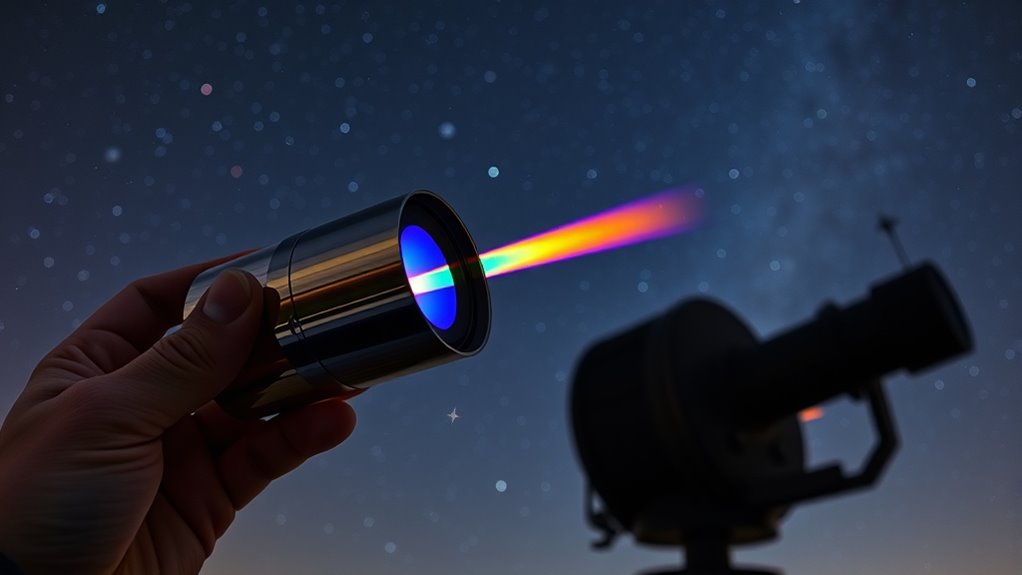
Using a spectroscope to analyze starlight lets you see how light disperses into colors, revealing a star’s chemical makeup and physical conditions. By examining spectral lines, you can identify elements and determine their quantities. Shifts in lines indicate whether a star moves toward or away from you, revealing its speed. The width and shape of lines tell you about temperature and turbulence in the star’s atmosphere. Keep exploring to discover more about what starlight can tell you.
Key Takeaways
- Disperse star light into its spectrum to identify characteristic spectral lines.
- Observe shifts in spectral lines to determine the star’s motion relative to Earth.
- Analyze line widths and shapes to assess stellar temperature and atmospheric conditions.
- Use spectral lines as fingerprints to identify elements and molecules in the star.
- Interpret spectral data to learn about the star’s composition, velocity, and physical properties.
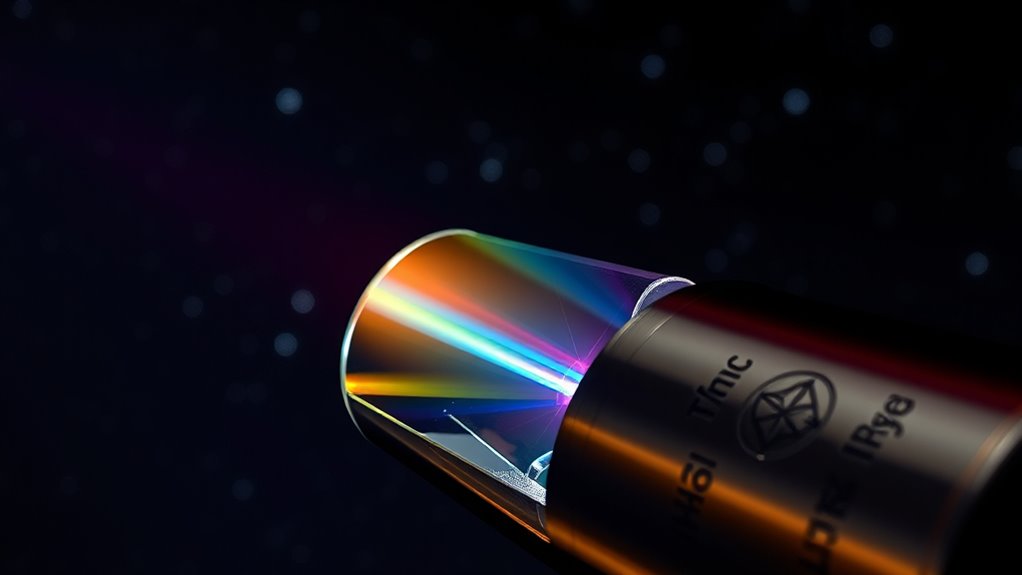

A spectroscope is a powerful tool that allows you to unravel the secrets hidden in starlight. When you point it at a star, it disperses the incoming light into its component colors, revealing a spectrum that contains crucial clues about the star’s composition and properties. Central to this analysis are spectral lines—dark or bright lines within the spectrum that stand out against the continuous background. These lines are signatures of specific elements and molecules, each corresponding to unique light absorption or emission processes. By studying these spectral lines, you can determine what elements are present in the star and even gauge other characteristics like temperature and density.
A spectroscope reveals star composition through spectral lines, identifying elements and properties by analyzing light absorption and emission.
As the star’s light passes through its outer layers, certain wavelengths get absorbed by elements in the star’s atmosphere. This light absorption results in dark absorption lines in the spectrum, which are key to understanding the star’s makeup. When you observe these spectral lines, you’re essentially seeing the fingerprints of the elements. The position of the lines indicates the specific element, while their intensity can tell you how much of that element exists. The pattern of spectral lines offers a detailed map of the star’s chemical composition, allowing you to identify heavy metals, gases, and other elements that make up the star.
Using a spectroscope, you’ll notice that the spectral lines are not static—they can shift due to various factors like the star’s motion relative to Earth. If the lines are shifted toward the red end of the spectrum, the star is moving away from you; if they shift toward the blue, it’s approaching. This Doppler effect enables you to measure the star’s velocity accurately. moreover, the width and shape of the spectral lines provide insights into the star’s temperature and pressure. Broader lines suggest higher temperatures or turbulent atmospheres, while narrow lines typically indicate calmer, cooler stellar environments.
In effect, by analyzing spectral lines created through light absorption, you gain a wealth of information about distant stars without ever leaving your observing spot. The spectroscope transforms faint starlight into a detailed story about the star’s life, composition, and motion. It’s a window into the universe, allowing you to decode the light that has traveled vast distances across space, revealing secrets hidden in the spectrum. With patience and careful observation, you can piece together the complex puzzle of stellar phenomena, making the invisible world of atoms and energy visible through the simple yet elegant mechanism of a spectroscope.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Spectroscope Identify Unknown Celestial Objects?
Yes, you can use a spectroscope to identify unknown celestial objects. It helps with spectral line identification, revealing specific wavelengths emitted or absorbed by the object. This process allows you to analyze the celestial composition, uncovering elements and molecules present. By examining the spectral patterns, you can determine whether the object is a star, galaxy, or nebula, providing valuable insights into its nature and properties.
What Are the Limitations of Amateur Spectroscopes?
While amateur spectroscopes open a window to the cosmos, they have their gentle limitations. You might find that calibration can drift over time, affecting accuracy, and spectral resolution isn’t as sharp as professional-grade tools. This means subtle details in starlight could be missed. Still, with patience and care, you can explore the universe’s secrets, appreciating the beauty of your instrument’s unique perspective.
How Does Temperature Affect Spectral Readings?
Temperature impacts your spectral readings by causing stellar temperature variations that lead to spectral shifts. As the star’s temperature changes, it alters the energy levels of atoms, shifting absorption lines. These shifts can make it seem like the star’s composition or velocity has changed. You need to account for these effects, especially in precise measurements, to avoid misinterpreting the data. Always consider stellar temperature when analyzing spectral data.
Can Spectroscopes Detect Exoplanets Directly?
You can’t detect exoplanets directly with a spectroscope alone, but you can observe their spectroscopic signatures through indirect methods. By analyzing shifts in a star’s spectral lines—like Doppler shifts—you can infer the presence of an orbiting exoplanet. These spectroscopic signatures help confirm exoplanet detection, revealing their existence and some characteristics, like mass and orbit, without directly imaging the planets themselves.
What Safety Precautions Are Necessary When Observing Stars?
You should never stare directly at bright stars or the sun, even through a spectroscope, as eye safety is vital. Ironically, light pollution can make stargazing feel safer, but it actually hampers your view and leads you to strain your eyes. Always use proper filters, avoid looking at intense light sources, and wear protective eyewear if necessary. Protect your vision while exploring the cosmos—your eyes are your most valuable tools.
Conclusion
By analyzing starlight with a spectroscope, you unlock the universe’s hidden secrets, revealing its true nature as if holding a cosmic decoder key. Each spectral line whispers stories of distant stars, inviting you to listen closely. Remember, in this dance of light and shadow, you hold the power to uncover the universe’s mysteries—if you dare to look. So, embrace your curiosity; the stars are waiting to tell you their secrets.